A blockchain is a public ledger of all Bitcoin transactions that have ever been executed. It is constantly growing as ‘completed’ blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. The blocks are added to the blockchain in a linear, chronological order. Each node (computer connected to the Bitcoin network using a client that performs the task of validating and relaying transactions) gets a copy of the blockchain, which gets downloaded automatically upon joining the Bitcoin network. The blockchain has complete information about the addresses and their balances right from the genesis block to the most recently completed block.

Blockchain formation.
The blockchain is seen as the main technological innovation of Bitcoin since it stands as proof of all the transactions on the network. A block is the ‘current’ part of a blockchain which records some or all of the recent transactions, and once completed goes into the blockchain as a permanent database. Each time a block gets completed, a new block is generated. There is a countless number of such blocks in the blockchain. So are the blocks randomly placed in a blockchain? No, they are linked to each other (like a chain) in proper linear, chronological order with every block containing a hash of the previous block.
To use conventional banking as an analogy, the blockchain is like a full history of banking transactions. Bitcoin transactions are entered chronologically in a blockchain just the way bank transactions are. Blocks, meanwhile, are like individual bank statements.
Based on the Bitcoin protocol, the blockchain database is shared by all nodes participating in a system. The full copy of the blockchain has records of every Bitcoin transaction ever executed. It can thus provide insight about facts like how much value belonged a particular address at any point in the past.
In the above representation, the main chain (black) consists of the longest series of blocks from the genesis block (green) to the current block. Orphan blocks (purple) exist outside of the main chain.
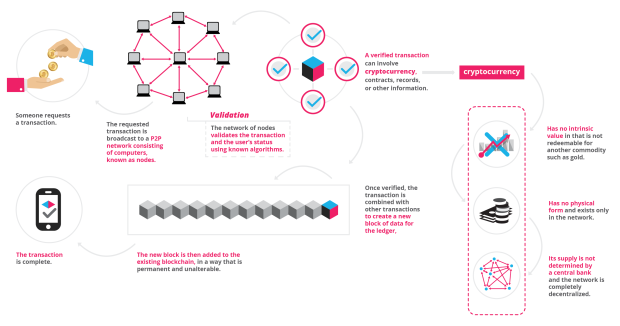
Working of Bitcoin and Blockchain
One thought on “What is Blockchain?”